1750–1914
Major Developments
- Questions of periodization
- Continuities and breaks, causes of changes from the previous period and within this period
- Changes in global commerce, communications, and technology
- Industrial Revolution (transformative effects on and differential timing in different societies; mutual relation of industrial and scientific developments; commonalities - which help cause 2)
- Changes in patterns of world trade (meaning changes in imperialism, which also helped cause 2)
- Demographic and environmental changes (migrations (including a special packet on it), the end of the Atlantic slave trade, new birthrate patterns (demographic explosion), food supply)
- Changes in social and gender structure (Industrial Revolution; commercial and demographic developments; emancipation of serfs/slaves; and tension between work patterns and ideas about gender, emerging new industrial labor systems)
- Political revolutions and independence movements; new
political ideas
- United States and Latin American independence movements
- Revolutions (United States (18th C., France, 18th C., Haiti, 19th C., Mexico 20th C., China 20th C.)
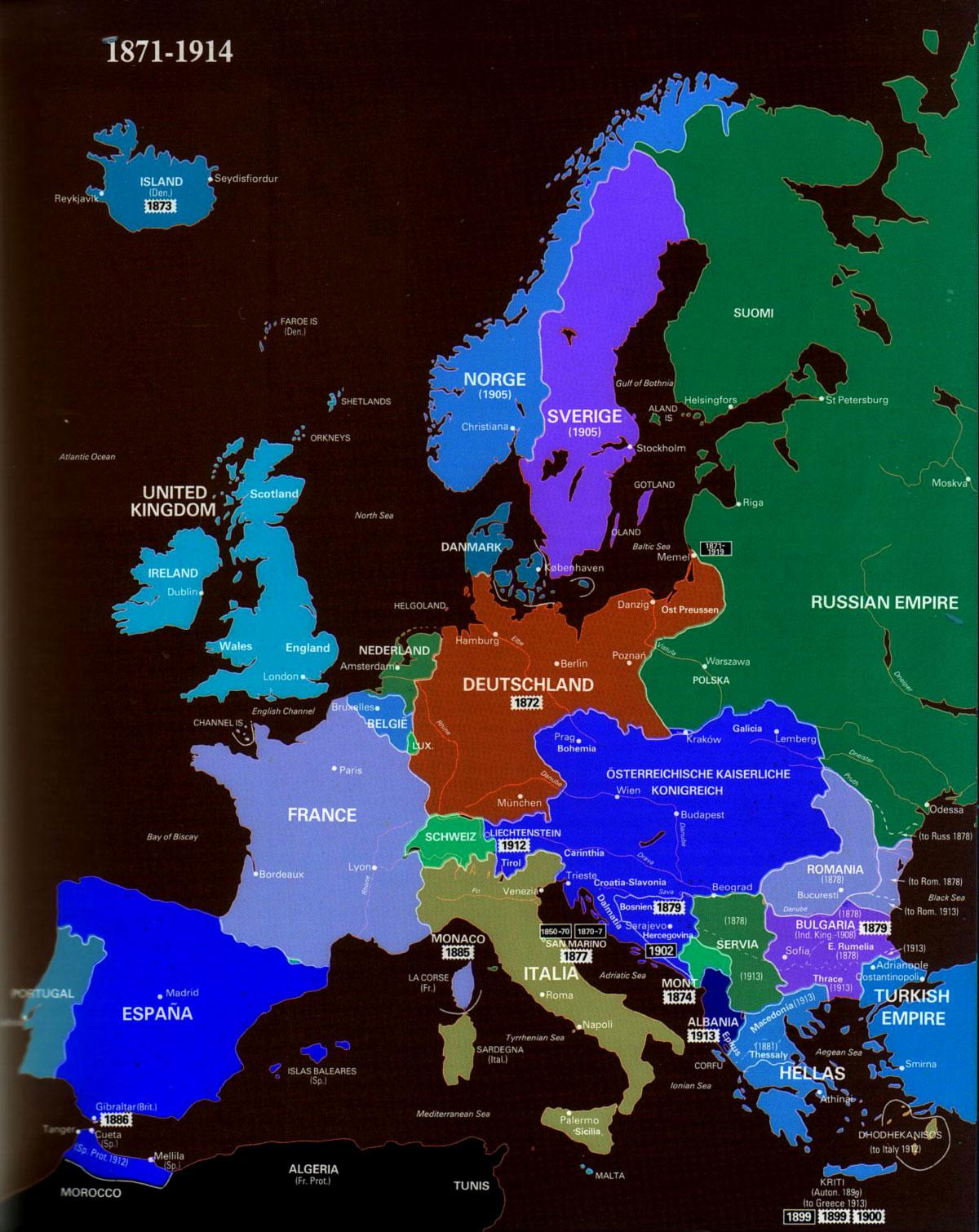
- Rise of nationalism, nation-states, and movements of political reform
- Rise of democracy and its limitations (as in, who didn't benefit?): reform; women; racism
- Rise of Western dominance (economic, political, social, cultural and artistic, patterns of expansion; imperialism and colonialism) and different cultural and political reactions (reform; resistance; rebellion; racism; nationalism, changing Euro ideologies on colonial administrations -like Social Darwinism- especially on the cultural, and also, because the new imperialism had more penetration through railroads, and today post-colonial vestiges exist. For example, in the old colonialism, it was the British East India Company working there. In the new, the 1857 Sepoy Rebellion took place agains the much more penetrative British administration. Good SPRITE Question.
- Diverse interpretations
- What are the debates over the utility of modernization theory as a framework for interpreting events in this period and the next?
- What are the debates about the causes of serf and slave emancipation in this period and how do these debates fit into broader comparisons of labor systems?
- What are the debates over the nature of women's roles in this period and how do these debates apply to industrialized areas and how do they apply in colonial societies?
- What are the debates over the causes of Euro/British technichal innovation vs. Asia/China?
Major Comparisons and Snapshots
- Compare the causes and early phases of the industrial revolution in western Europe and Japan
- Comparative revolutions (compare the Haitian and French Revolutions)
- Compare reaction to foreign interference in: the Ottoman Empire, China, India (Rom Roy, Ghandi), and Japan
- Compare nationalism in the following pairs: China and Japan, Indian Congress Movement and the Pan Africanism of Marcus Garvey, Italy and the Egypt of Muhammad Ali
- Explain forms of Western intervention in Latin America, Africa, and Southeast Asia
- Compare the roles and conditions of women in the upper/middle classes with peasantry/working class in western Europe
Examples of What You Need to Know
Below are examples of the types of information you are expected to know contrasted with examples of those things you are not expected to know for the multiple-choice section.
- Causes of Latin American independence movements, but not specific protagonists.
- The French Revolution of 1789, but not the Revolution of 1830
- Meiji Restoration, but not Iranian Constitutional Revolution
- Causes of Latin American independence movements, but not specific protagonists
- Boxer Rebellion, but not the Crimean War
- Suez Canal, but not the Erie Canal
- Muhammad Ali, but not Isma'il
- Marxism, but not Utopian socialism
- Social Darwinism, but not Herbert Spencer
- Women's emancipation movements, but not specific suffragists.







