
. POSTCLASSICAL (MEDIEVAL) ASIA .
SUI, TANG AND SONG CHINA

The Grand Canal was finished in the postclassical period (Sui-Tang-Song, 600-1200)
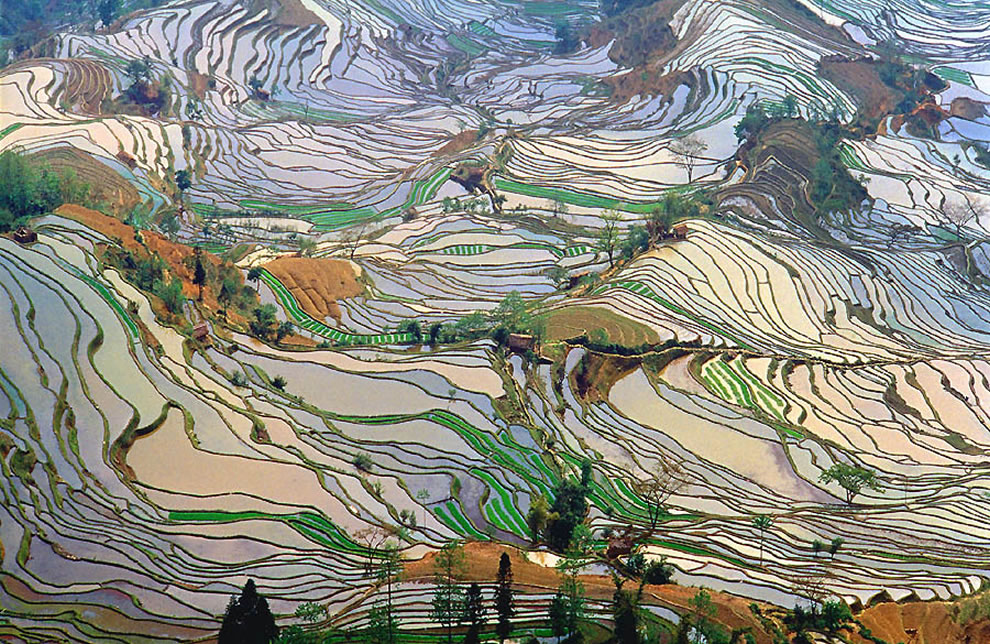

Agricultural land like these rice paddies was re-distributed by the government in the Equal-Field System
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equal-field_system. Soon fast-ripening rice would affect Chinese economics.

The bureaucracy of merit idea meant that many took the civil service exam to try and get a job
The imperial exam was founded by the Sui in 605: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Imperial_examination
The Mongols would abolish it in the 1300s but it would return under the Ming and Qing until recent times.
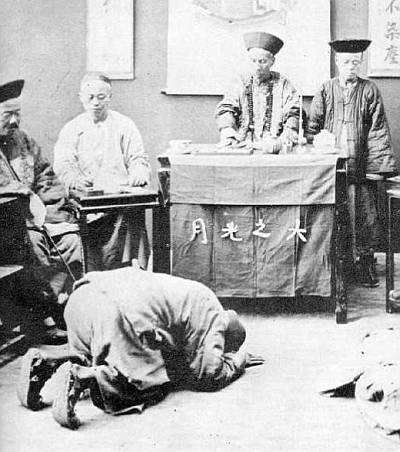

The kowtow performed before the imperial Chinese court
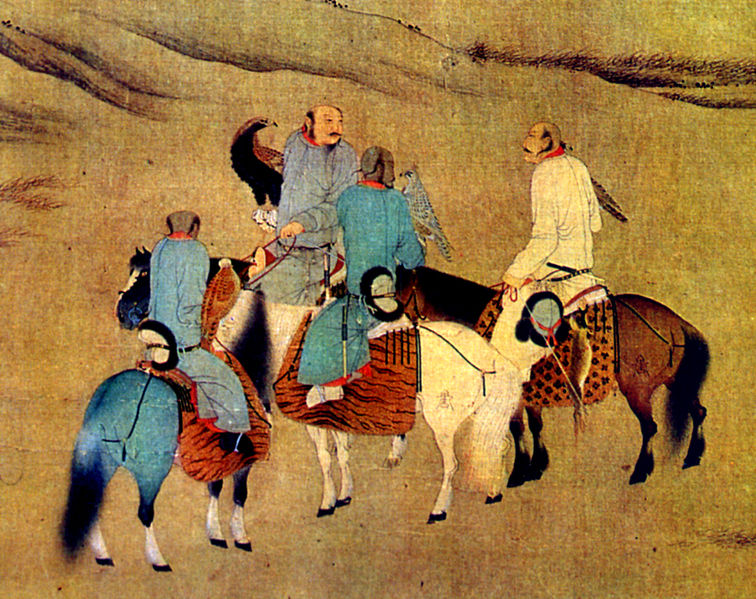

The Khitan people use eagles to help in hunting during the Song Dynasty
China's local barbarians: Khitans, Jurchens and Manchus

Goryeo (Korea) - Khitan War: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Khitan_people

Jurchen armor- all three lived north of Song China: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jurchen_people

Urbanization: Chang'an had 2 million people... biggest city in the world during the postclassical period
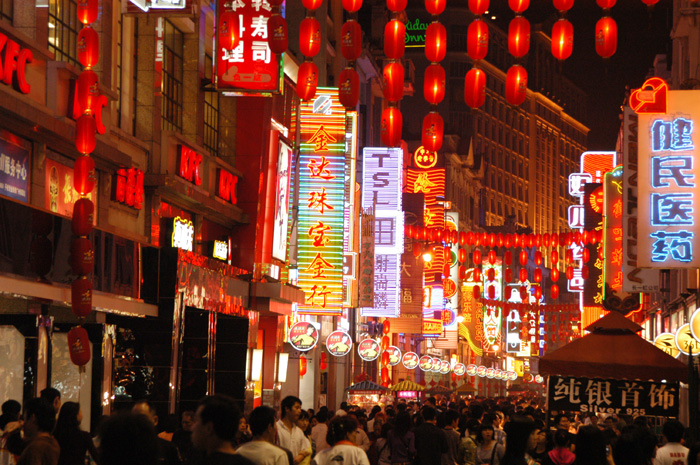

Guangzhou (Canton) had restaurants, taverns, noodle shops, tea houses, brothels, gardens, music shops and more
Li Bai's urban poems were read and played out here as a favorite form of literary engagement during the Tang-Song.


Foot binding, a sign of patriarchal society in China, mostly affected aristocratic women
Earliest written formula for gunpowder, from the 1000s AD in China:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_gunpowder

Song wooden blocks used to print copies of text

Buddhist caves in Dunhuang: Song era Confucians like Buddhism- darma is translated as 'dao'!
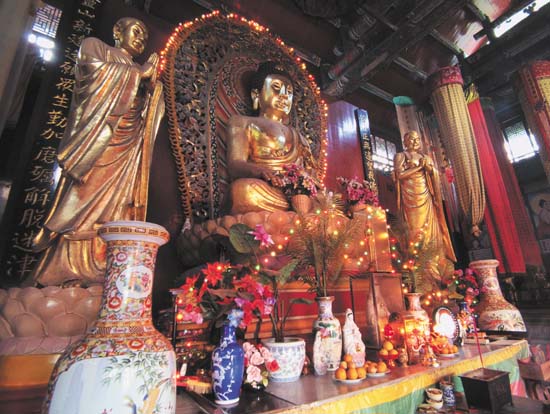

Zen Buddhism is characterized by medidation, flashes of insight, but was persecuted by Daoist
SILLA KOREA, NARA / HEIAN JAPAN AND NAM VIET
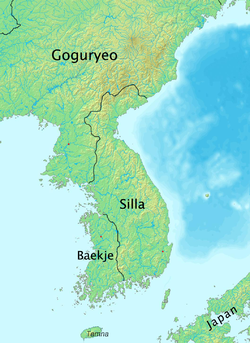
Korea is in 'the middle' of the East Asian powers, China and Japan
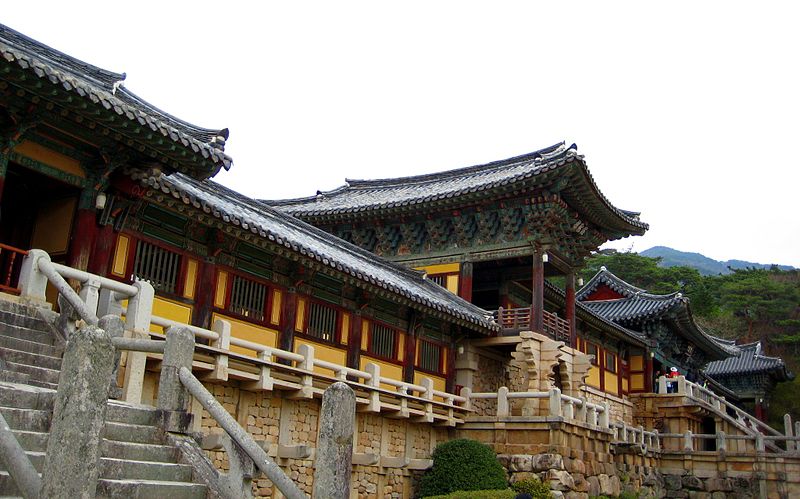

The Bulguksa Temple in Korea completed by the Silla in 774
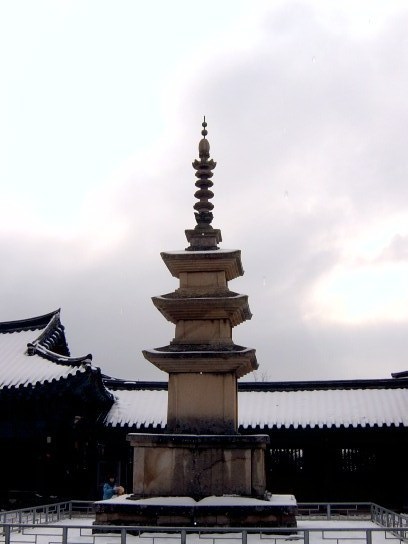

The Seokgatap monument at the temple
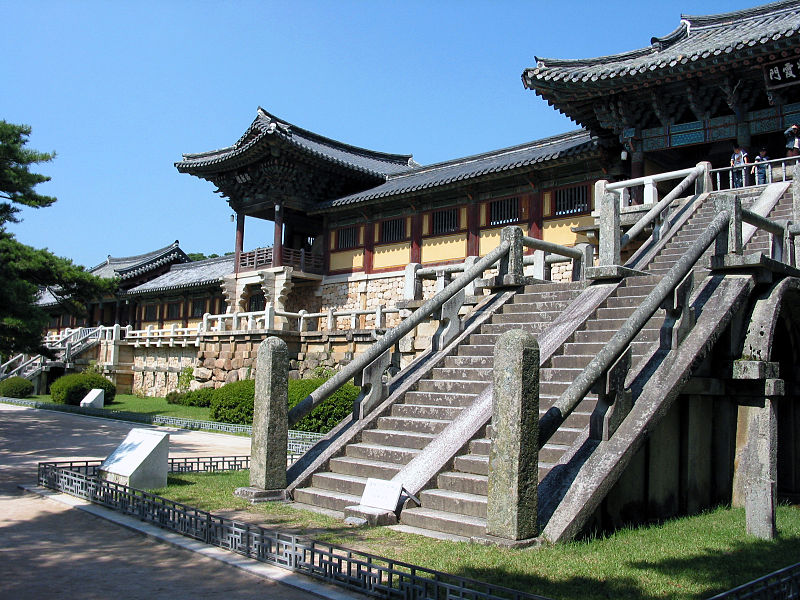

Blue Cloud and White Cloud Bridges are in the foreground, the Lotus Flower and Seven Treasures Bridges are in the background.
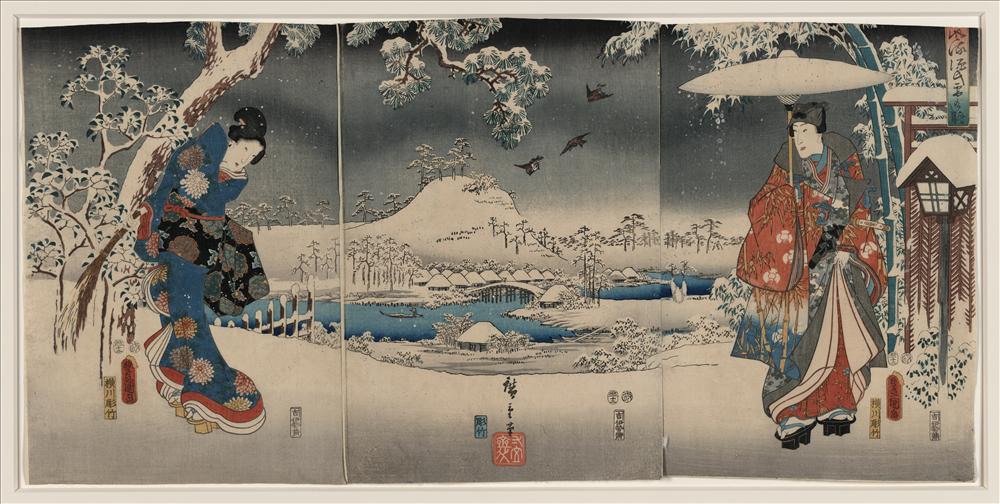

A scene from Lady Murasaki's Tale of the Genji

Bushido Code of the Samurai

The first capital of Japan (700s), Nara

The Todaiji temple (Buddhist) in Nara, Japan: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Historic_Monuments_of_Ancient_Nara
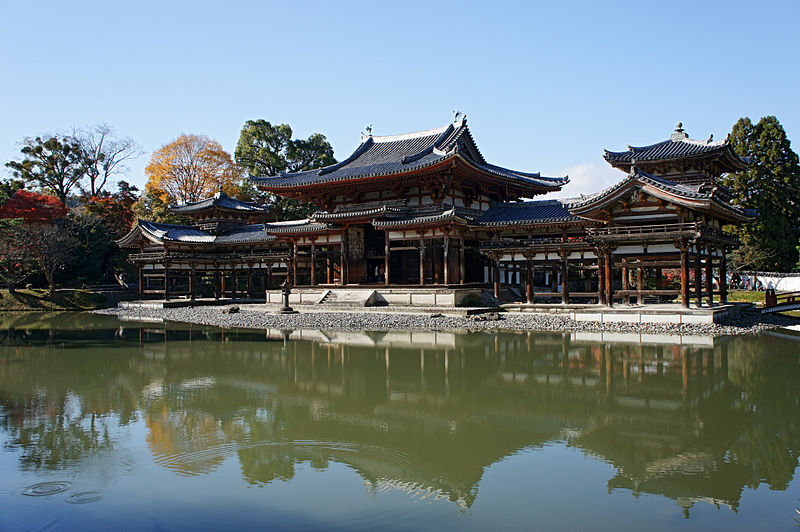

The Heian Period succeeded the Nara, and the capital was moved here, to Kyoto
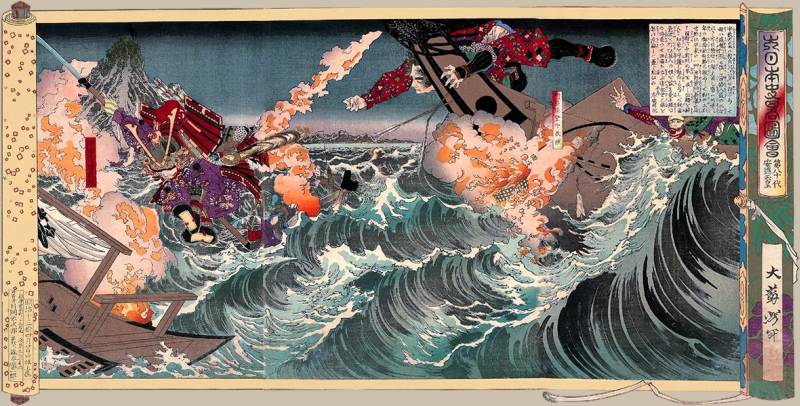

The Battle of DanNoUra, in 1185, which sealed the fate for the Samurai Heike clan, who were defeated by the Genji

The interesting Heike Crab which appeared over time after the battle
VIET NAM / INDOCHINA
An ancient stele containing Sanskrit writing is the only existant one dealing with the Funan Kingdom (6th century Indochina)
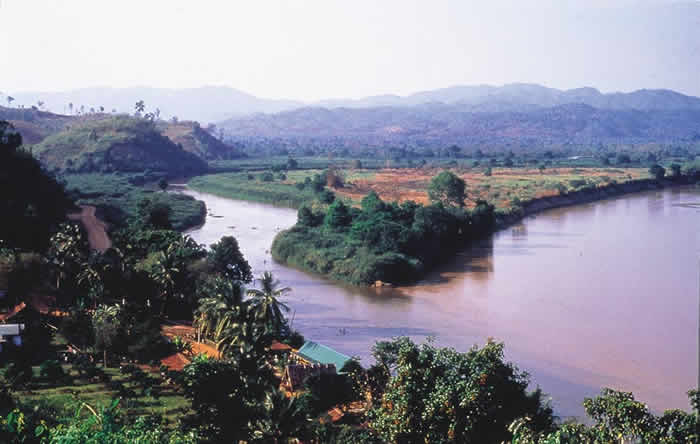

The Funan state was located on the Mekong River in today's Vietnam

The Srivajaya kingdom based on Sumatra (Indonesia) controlled the Indies from the 7th to the 13th centuries
It was eclipsed by Chola India but its legacy can be seen in Buddhist architecture in places like Thailand and Malaysia
The Malaccan Empire resulted from Islamic expansion to Srivajaya, this is the Sultan's residence
Zheng He's fleet stopped here as well in the early 15th century
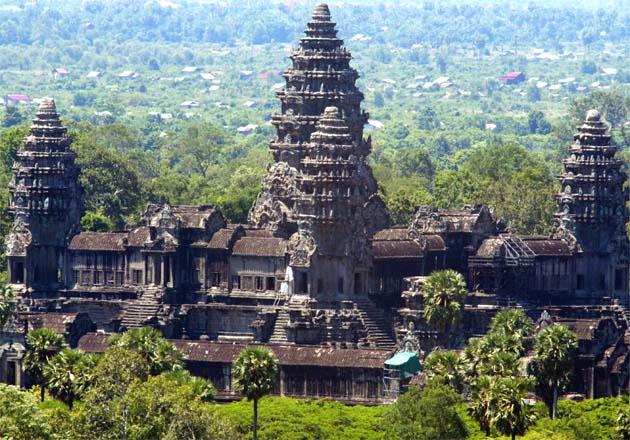

The Angkor Wat Buddhist temple located in today's Cambodia is the centerpiece of the ancient Angkor culture
The Khmer Empire's capital, it lasted from 800-1431 before declining because of religious problems and an
inability to further control the water irrigation system (meaning floods were more frequent), as well as the Plague

The famous serene faces of Angkor Wat show Buddhist harmony with life

The Khmer Empire was rival to the Srivajaya, its religions were Hinduism, Buddhism
It covered Thailand, Cambodia, Viet Nam and parts of Malaysia before being reclaimed by the jungle
Post-Gupta India
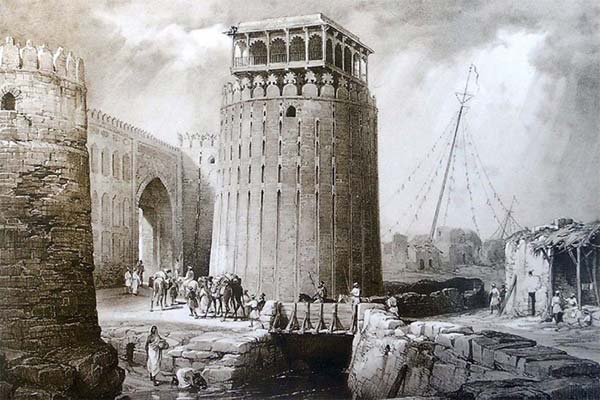

Signal of Harsha's decline: Abbasid castle complex built after the conquest of the Sind at Hyderabad

Mahmud of Ghazni holding court in India after looting Punjab and destroying Hindu temples
Islamic expansion in the postclassical period went east into India and China, south to Africa (Axum) and north to Byzantium
In all, 25% of India would covert to Islam

The Delhi Sultanate kept India free from the Mongols in the 1200s but was later taken by the Afghan Moguls
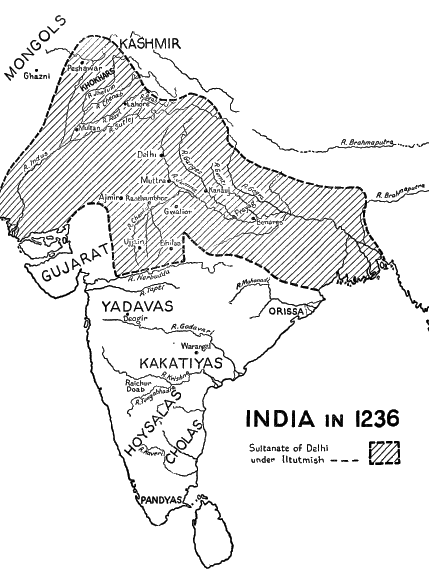
A professional does a SPRITE chart for the Delhi Sultanate:
http://chip.choate.edu/bbcswebdav/institution/HPRSS/WorldTech/tfprojects2002/delhiAblock/Economic%20Activity.htm


Hinduism developed energetically after the Islamic incursion into north India, and Buddhism declined in India
Here Vishnu (left) and Siva gained more roles, and cults developed around both of them, while Shankara harmonized Hinduism
and Ramanuja taught union with Vishnu was possible. Nevertheless, many lower caste people converted to Islam during the Sultanate
Guru Kabir even taught that Vishnu, Siva and Allah as the same deity, and the Bhakti movement stressed Muslim-Hindu unity
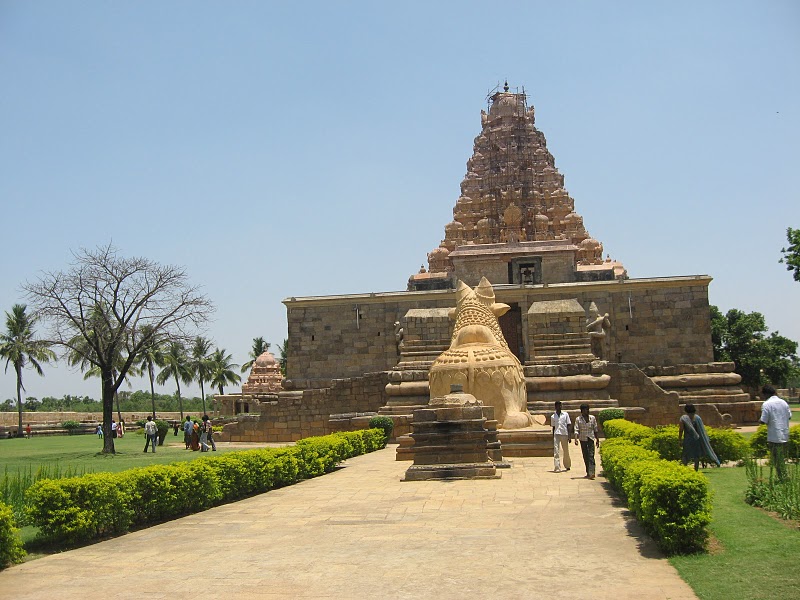

India's Chola Dynasty ruled the southern part of the subcontinent while the Delhi Sultanate ruled the north

Siva Idol at Brihadeeswara Temple
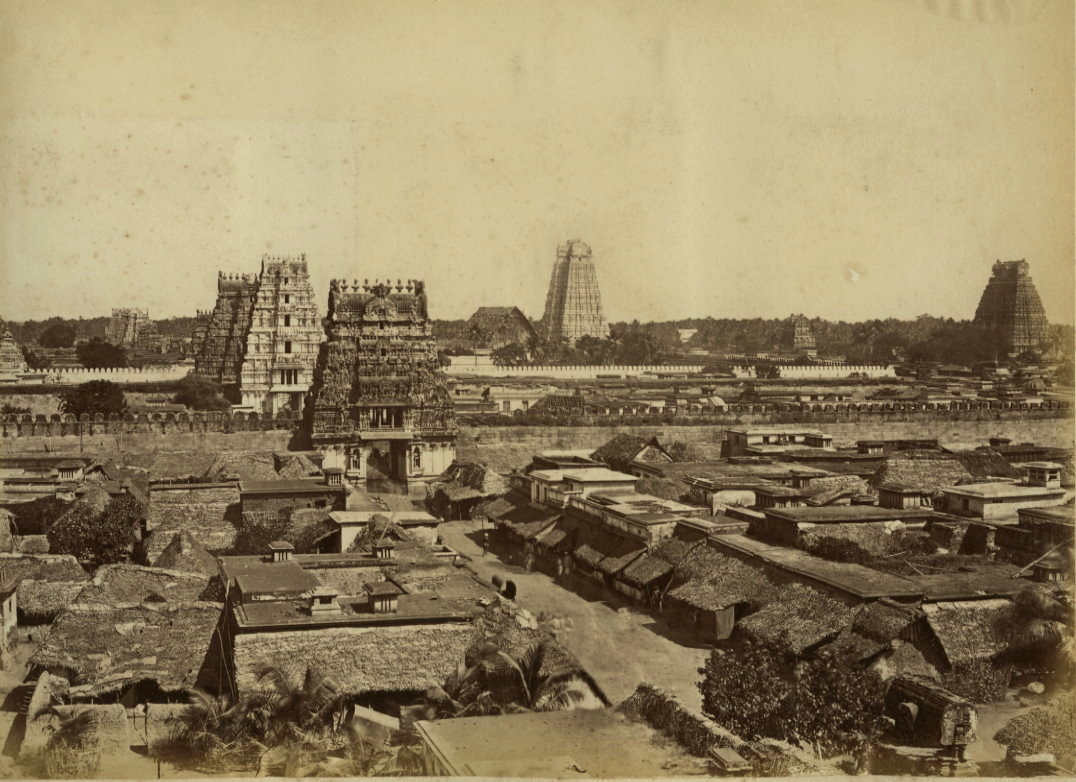

Trichanopoly as it was called by the British, is a temple complex in southern India build by the Cholas
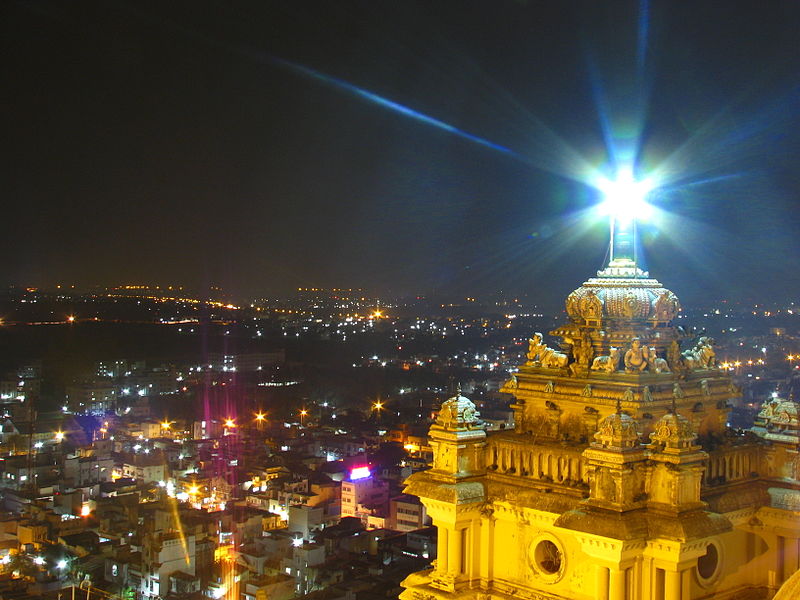

Mystical India's tradition lives on today in the Rockfort (Ucchi Pillayar)
a temple built on an outcropping of rock 3 billion years old
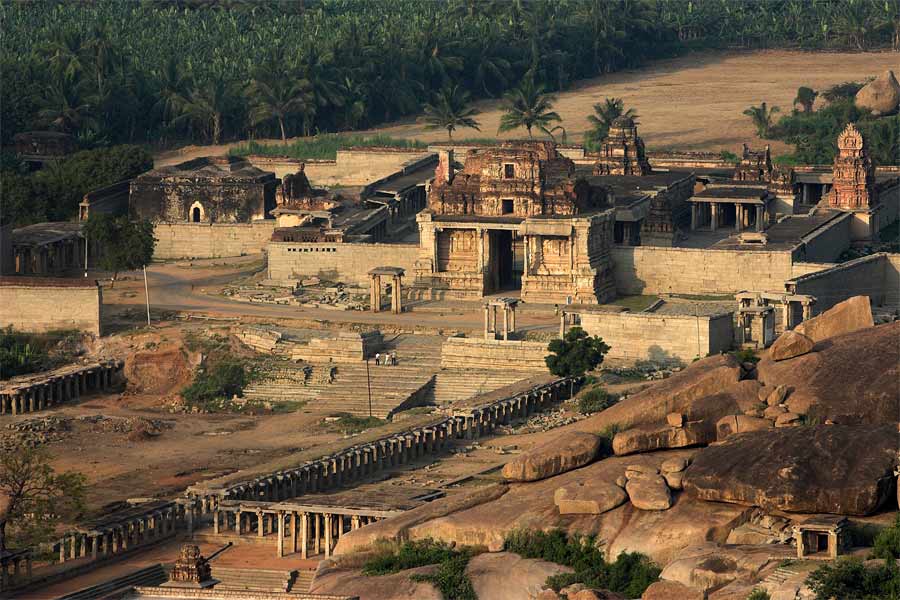

The Krishna Temple built in the 1300s was the centerpiece of India's Vijayanagar (Hampi) dynasty-
the largest, wealthiest and most powerful Hindu Kingdom in southern India following the Cholas
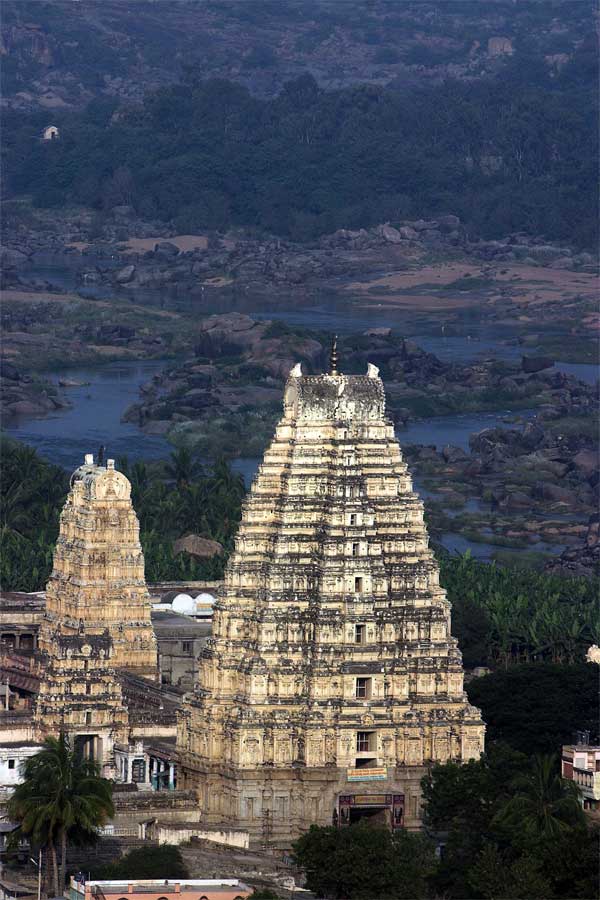

Pampapati Temple nearby- original Hindu architecture from before the conquest by the Moghuls
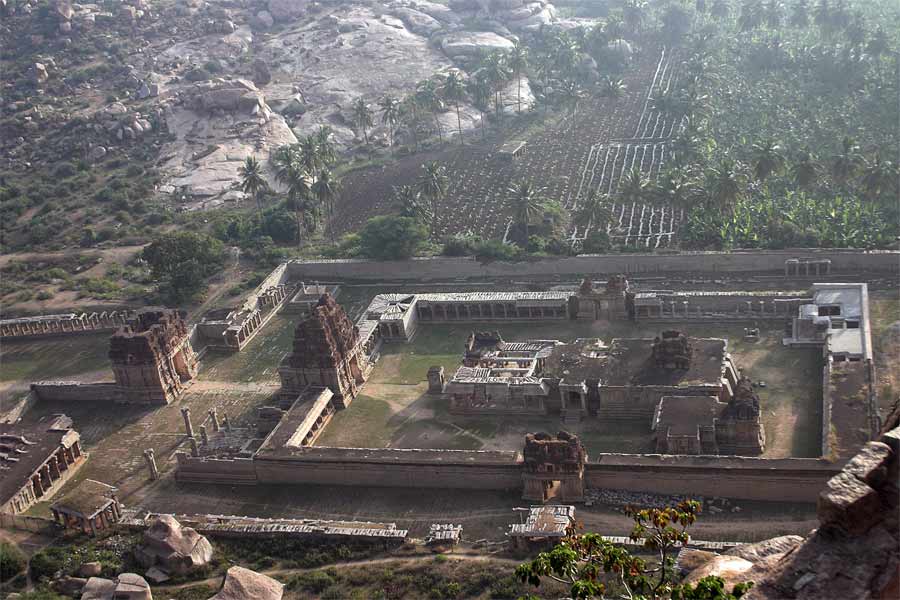

Today Vijayanagar (City of Victory) is mostly a ruin
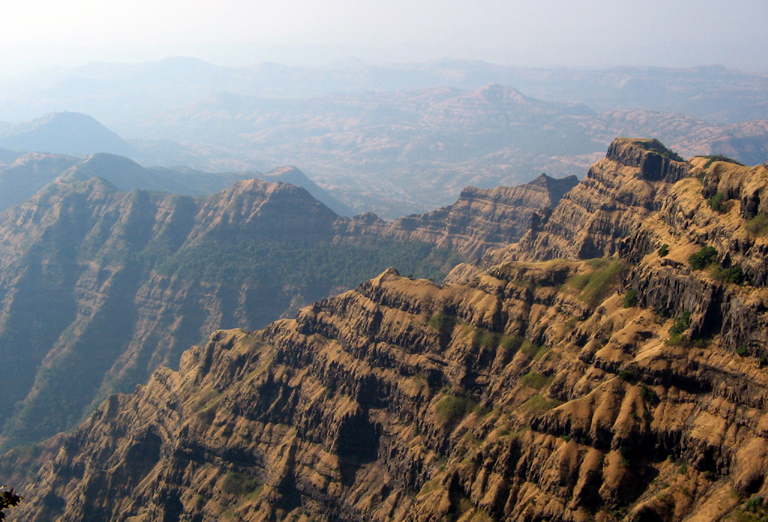

NASA recognizes India's central Deccan Plateau as one of the amazing geological landforms in the world
http://rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/Sect17/Sect17_3.html
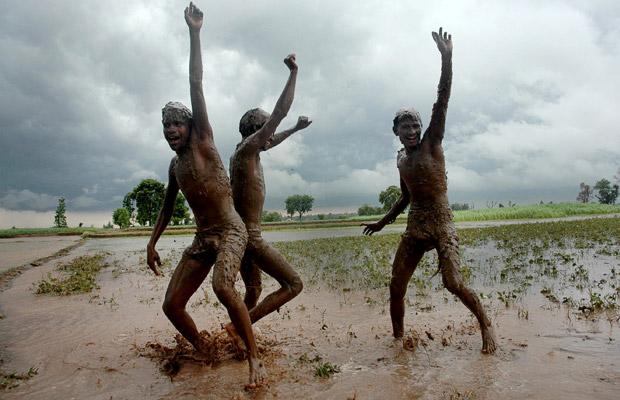

Indian boys having fun in the Monsoon season
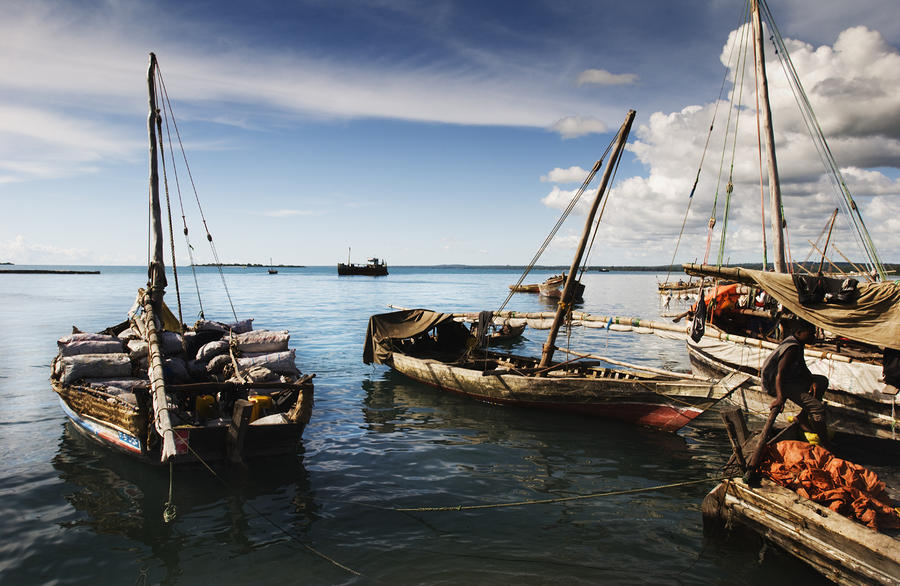

During the postclassical age in the Indian Ocean, Arabic Dhows like these had to negociate the Monsoons

Calicut, India became a major hub of the Indian Ocean trade linking China and the Indies with India, Persia, Arabia and Africa
In this emporium could be found cotton textiles, refined sugar, tanned products and high carbon steel
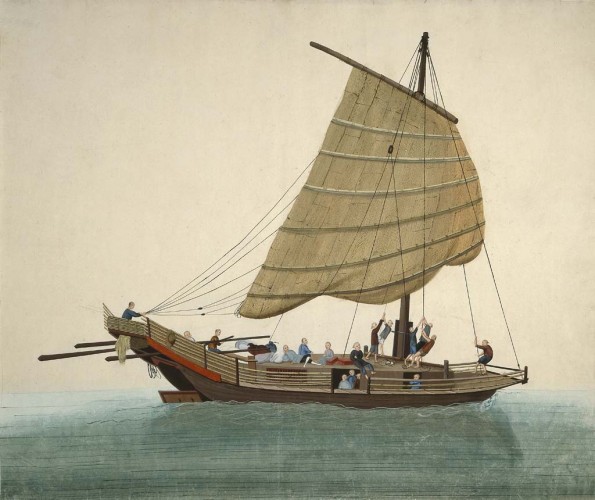

Chinese Junks could be found on the Indian Ocean as well, carrying 1000 tons
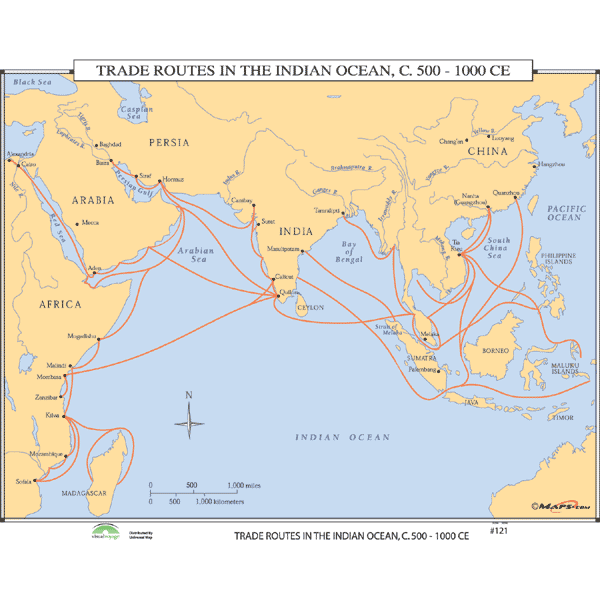
Trade routes during the heyday of the postclassical Indian Ocean trade
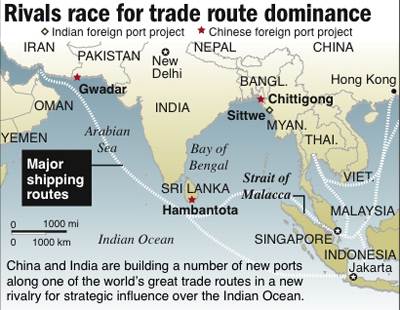
Today the Indian Ocean trade is still a coveted arena of competition between world powers!
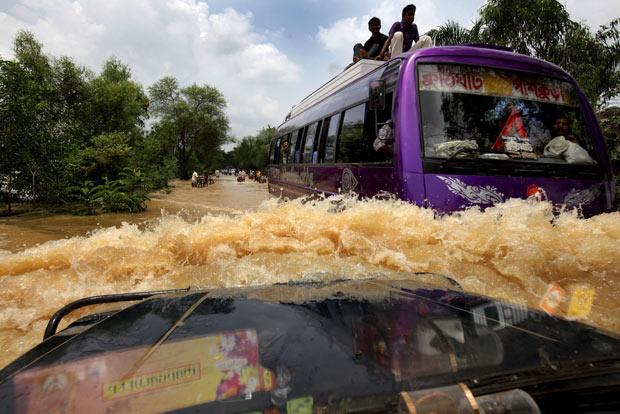

Ancient rain and flood patterns mix with modern society to create an interesting scene,
reminding us that travelers still have to negociate the Monsoon season
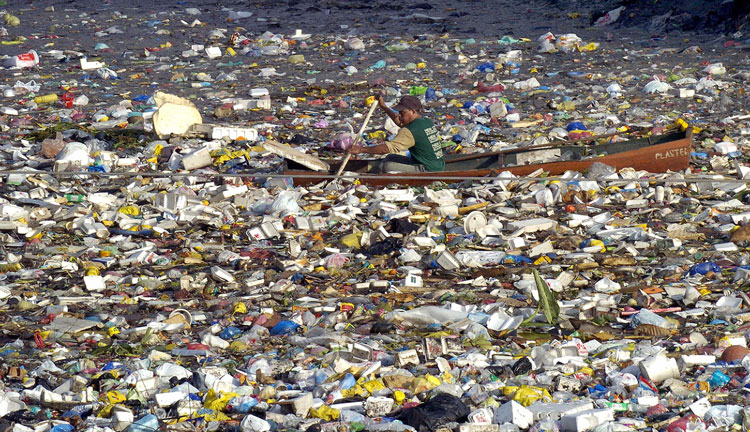

With four-five billion people living along the coastlines of Asia and Africa, much trash is just thrown out into the sea
During the postclassical period, greater India had 105 million people, and today the number is 20x that figure
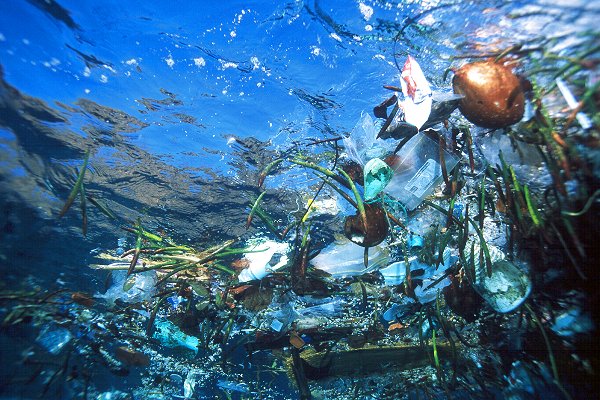


Much of it winds up in the middle of the Indian and Pacific Oceans in places called gyres
Site Design: David Tamm